- Introduction
 Cattle
Cattle
 Dog
Dog
 Goat
Goat
 Horse
Horse
 Sheep
Sheep
 Pigs
Pigs
- Genotype SNPs
- Remission of samples
INTRODUCTION
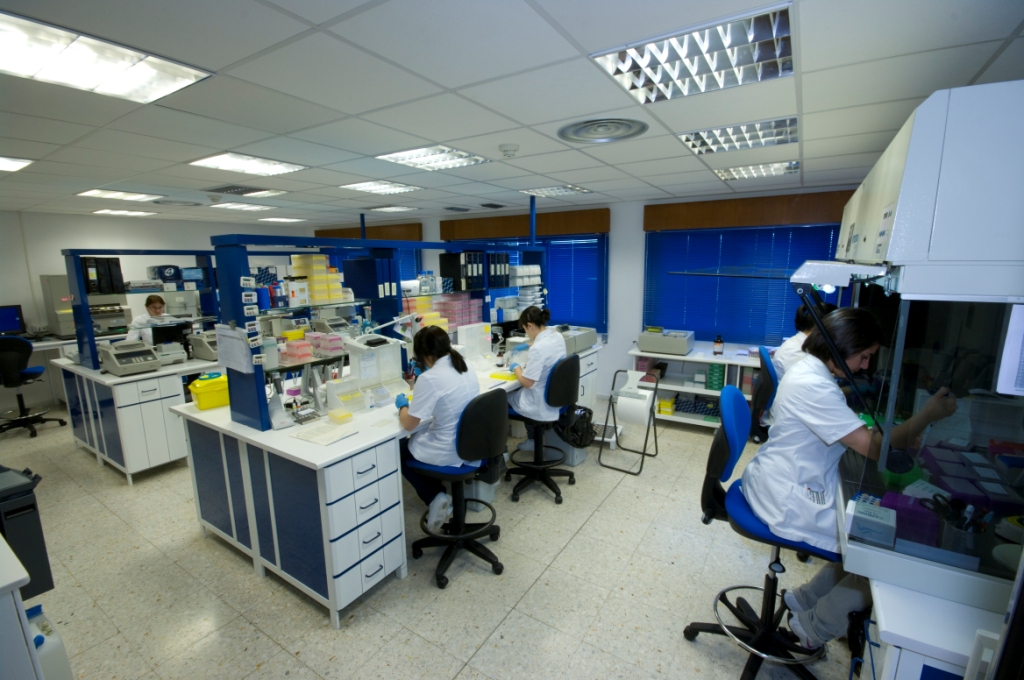
DNA BIOTECHNOLOGY TO LIVESTOCK FARMING SERVICE
The great development reached by the Molecular Genetic in last decades, has determined a high knowledge of the genome of the different species. The GENOME projects, whose principal aim is to know the DNA sequence of the different animal species and the relative position of every gene in the chromosomes, are contributing in an important way to these facts. These researches are generating numerous applications in Veterinary, since they are allowing the location of genes involved in productive characters or responsible of genetic diseases or anomalies, and a best knowledge of the genetic variability, through the study of the molecular markers.
Xenética Fontao S.A. is a company specialized in genetic improvement, which manages the Galician Artificial Insemination Centre. In 1999, the molecular genetic laboratory was founded in order to offer new services using the DNA biotechnology in health and livestock production. En 2001 this lab was registered as institutional member of I.S.A.G. (International Society for Animal Genetics), with the laboratorial code 84434.
MOLECULAR GENETIC LAB SERVICES
DNA profile and parentage verification
The genetic identification and the establishment of parentage testing allow the liability and credibility of the Herd Books in the different animal breeds. Parentage verification is a genetic test that is used to check the animal pedigree. Recently the used methods are based on high polymorphic DNA markers analysis such as microsatellites, also called STRs (Short Tandem Repeats).
Microsatellite markers are particularly suitable to these proves by their properties: abundance in the genome, Mendelian inheritance with codominant nature, high polymorphism or elevated number of alleles and experimental reproducibility, easy identification by PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction), with possibility of multiplexing and suitability to use in the new automatic genetic analyzers. In this way, it is very important the role of the I.S.A.G. (International Society for Animal Genetics), a scientific society that provides a forum for the exchange of information between members, in order to co-ordinate the different laboratories and standardise protocols, nomenclatures and selection of international microsatellite panels, allowing that the obtained results by the different researchers are objective and comparable.
Meat traceability
The Quality Certification Systems as Geographical Indication, Protected Designation of Origin and Guaranteed Traditional Specialities must be an instrument that gives answers to them, offering the best guarantees and objective information to the consumers and economic agents of the sector dedicated to the commercialisation of beef.
The using of DNA markers allows us to assure a traceability of 100% in the beef industry from the animal to the dish. To the sampling is not necessary any significant change in the habitual practice in the meat transformation industry, because DNA is a very steady molecule resistant to chemical and mechanical treatments.
Diagnosis of genetic diseases
The interest of diagnosis is based on the detection of the hereditary anomalies of the carrier animals, above all if the animals are the ones employed as reproductive in the programs of genetic improvement (semen, embryos and oocyte producers) due to the great dissemination they provoke in population.
Normally, the genetic diseases are inherited as recessives. These diseases occur when an embryo inherits genes with specific mutations from carrier parents, both clinically normal. The levels of inbreeding within a population establish the prevalence of such diseases, but generally, specific genetic diseases are more common in particular breeds. There are a big number of DNA tests with very accurate to identify carriers of responsible specific mutations of the genetic diseases in the different animal species.
Genetic anomalies: Freemartinism
This causes infertility in the female calf born twin with a male and it is recognized as one of the most severe forms of sexual abnormality in cattle. Freemartinism cannot be prevented, but it is possible to make a precocious diagnosis after the birth using PCR technology.
Milk proteins
Numerous researches have shown important associations between milk protein genetic variants and milk production traits (manufacturing properties of milk and cheese production). Because of these associations, since several years ago, the interest in selecting for favourable milk protein genotypes was considerable.
Coat colour
Holstein cattle breed is divided in two subpopulations: Black Holstein (BW) and Red Holstein, this one can be Red and White (RW) or Black-Red (BR). The producer interest in Red Holsteins has been varied along the years, but nowadays the breed is experiencing a renewed interest with selection for Red Holstein.
Scrapie genetic susceptibility
Several scientific researches evident a relation between the genetic characters and the natural resistance of some animals to suffer different diseases. Scrapie is a progressive neurodegenerative disease of sheep and goats, included in the group of Transmissible Spongiform Encephalopathies (TSEs). Common to all TSE diseases is the accumulation of an abnormal form of the normal prion protein (PrP), primarily in the brain and spinal cord. This abnormal form is derived from a conformational change in the cellular prion protein (PrPC) to PrPSC. In its abnormal configuration PrPSC pis infectious, insoluble and extremely resistant to proteolytic enzymes.
CONTACT:The great development reached by the Molecular Genetic in last decades, has determined a high knowledge of the genome of the different species. The GENOME projects, whose principal aim is to know the DNA sequence of the different animal species and the relative position of every gene in the chromosomes, are contributing in an important way to these facts. These researches are generating numerous applications in Veterinary, since they are allowing the location of genes involved in productive characters or responsible of genetic diseases or anomalies, and a best knowledge of the genetic variability, through the study of the molecular markers.
Xenética Fontao S.A. is a company specialized in genetic improvement, which manages the Galician Artificial Insemination Centre. In 1999, the molecular genetic laboratory was founded in order to offer new services using the DNA biotechnology in health and livestock production. En 2001 this lab was registered as institutional member of I.S.A.G. (International Society for Animal Genetics), with the laboratorial code 84434.
MOLECULAR GENETIC LAB SERVICES
DNA profile and parentage verification
The genetic identification and the establishment of parentage testing allow the liability and credibility of the Herd Books in the different animal breeds. Parentage verification is a genetic test that is used to check the animal pedigree. Recently the used methods are based on high polymorphic DNA markers analysis such as microsatellites, also called STRs (Short Tandem Repeats).
Microsatellite markers are particularly suitable to these proves by their properties: abundance in the genome, Mendelian inheritance with codominant nature, high polymorphism or elevated number of alleles and experimental reproducibility, easy identification by PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction), with possibility of multiplexing and suitability to use in the new automatic genetic analyzers. In this way, it is very important the role of the I.S.A.G. (International Society for Animal Genetics), a scientific society that provides a forum for the exchange of information between members, in order to co-ordinate the different laboratories and standardise protocols, nomenclatures and selection of international microsatellite panels, allowing that the obtained results by the different researchers are objective and comparable.
Meat traceability
The Quality Certification Systems as Geographical Indication, Protected Designation of Origin and Guaranteed Traditional Specialities must be an instrument that gives answers to them, offering the best guarantees and objective information to the consumers and economic agents of the sector dedicated to the commercialisation of beef.
The using of DNA markers allows us to assure a traceability of 100% in the beef industry from the animal to the dish. To the sampling is not necessary any significant change in the habitual practice in the meat transformation industry, because DNA is a very steady molecule resistant to chemical and mechanical treatments.
Diagnosis of genetic diseases
The interest of diagnosis is based on the detection of the hereditary anomalies of the carrier animals, above all if the animals are the ones employed as reproductive in the programs of genetic improvement (semen, embryos and oocyte producers) due to the great dissemination they provoke in population.
Normally, the genetic diseases are inherited as recessives. These diseases occur when an embryo inherits genes with specific mutations from carrier parents, both clinically normal. The levels of inbreeding within a population establish the prevalence of such diseases, but generally, specific genetic diseases are more common in particular breeds. There are a big number of DNA tests with very accurate to identify carriers of responsible specific mutations of the genetic diseases in the different animal species.
Genetic anomalies: Freemartinism
This causes infertility in the female calf born twin with a male and it is recognized as one of the most severe forms of sexual abnormality in cattle. Freemartinism cannot be prevented, but it is possible to make a precocious diagnosis after the birth using PCR technology.
Milk proteins
Numerous researches have shown important associations between milk protein genetic variants and milk production traits (manufacturing properties of milk and cheese production). Because of these associations, since several years ago, the interest in selecting for favourable milk protein genotypes was considerable.
Coat colour
Holstein cattle breed is divided in two subpopulations: Black Holstein (BW) and Red Holstein, this one can be Red and White (RW) or Black-Red (BR). The producer interest in Red Holsteins has been varied along the years, but nowadays the breed is experiencing a renewed interest with selection for Red Holstein.
Scrapie genetic susceptibility
Several scientific researches evident a relation between the genetic characters and the natural resistance of some animals to suffer different diseases. Scrapie is a progressive neurodegenerative disease of sheep and goats, included in the group of Transmissible Spongiform Encephalopathies (TSEs). Common to all TSE diseases is the accumulation of an abnormal form of the normal prion protein (PrP), primarily in the brain and spinal cord. This abnormal form is derived from a conformational change in the cellular prion protein (PrPC) to PrPSC. In its abnormal configuration PrPSC pis infectious, insoluble and extremely resistant to proteolytic enzymes.
lxmbovino@xeneticafontao.com
xfontao@xeneticafontao.com
javier.lopez.viana@xunta.gal
 |
www.xeneticafontao.com